Files
Description
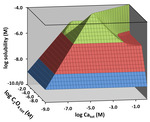
A new 3-D graphical representation for the solubility of sparingly soluble salts in aqueous solutions has been developed utilizing a new composition grid. In this case, the x-axis carries the concentration of the salt’s cation (usually a metal) and the y-axis holds the concentration of the salt’s anion. Plotted above the grid are a salt’s solubility, individual species concentrations or distribution coefficients. Three levels of sophistication in the descriptive chemistry are discussed. In Case 1, the only dissolved species included are the cation and anion present in the salt’s solubility product expression, the Ksp. Case 2 adds the possibility of ion pairs or neutral complexes. Finally, Case 3 encompasses all complexes for which thermodynamic constants are available. Example systems include the 1:1 AgCl and the 1:2 PbI2 salts. The composition grid approach addresses not only the solubility of a solid salt in pure water, but essentially all other feasible conditions in which one or the other of the component ions is present in the dissolving liquid phase. Case 1 gives rise to 3-D solubility surfaces (topos) that have a pyramidal shape. Case 2 possesses plateaus under saturated conditions where the concentration of the ion pair or neutral complex dominates. Case 3 can add extra ramps under saturated conditions when other complexes become important. A comparison of the topos from all three cases for a given salt allows the user to see the effects of incompletely capturing the possible chemical processes that contribute to solubility. The Case 3 solubility maximum can be significantly larger than that for Case 1. In the AgCl system, for example, the maximum solubility was 12.5 times greater than that predicted for Case 1. Included as supplementary files for the chapter are the downloadable Solubility TOPOS software (an Excel workbook), a PowerPoint lecture, teaching materials, a detailed description of the formulas and algorithms used to solve for solubility, and a Visual Basic code listing.
Publication Date
11-2023
Document Type
Book
Rights
© 2023 Garon C. Smith and Md Mainul Hossain
Creative Commons License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
Disciplines
Chemistry
Recommended Citation
Smith, Garon C. and Hossain, Md Mainul, "Chapter 4.1: Visualizing the Solubility of Salts Via 3-D Topo Surfaces: Pyramids with Ridges and Plateaus" (2023). Water Topos: A 3-D Trend Surface Approach to Viewing and Teaching Aqueous Equilibrium Chemistry. 10.
https://scholarworks.umt.edu/topos/10