Files
Description
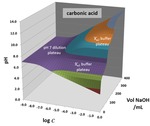
3-D topos can be generated to visualize how pH behaves during titration and dilution procedures. The surfaces are constructed by plotting computed pH values above a composition grid with volume of base added in one direction and overall system dilution on the other. Surficial features correspond to behavior in aqueous solutions. Equivalence point breaks become cliffs that pinch out with dilution. Buffer effects become plateaus. Dilution alone generates 45o ramps. Sample surfaces are analyzed for acetic acid, CH3COOH (a weak monoprotic acid); hydrochloric acid, HCl (a strong acid); oxalic acid, HOOCCOOH (a weak diprotic acid) and L-histidine dihydrochloride, C6H9N3O2 ∙2HCl (a weak triprotic acid). Two rarely discussed pH behaviors are illuminated – buffering against dilution and pseudo-buffering. The pH TOPOS software to generate other surfaces is provided as a downloadable Excel workbook. Other downloadable files include a PowerPoint lecture and teaching suggestions for pH topo surfaces.
Publication Date
11-2020
Document Type
Book
Rights
© 2020 Garon C. Smith, Md Mainul Hossain, and Patrick MacCarthy
Creative Commons License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
Disciplines
Chemistry
Recommended Citation
Smith, Garon C.; Hossain, Md Mainul; and MacCarthy, Patrick, "Chapter 1.1: 3-D Surface Visualization of pH Titration “Topos”: Equivalence Point Cliffs, Dilution Ramps and Buffer Plateaus" (2020). Water Topos: A 3-D Trend Surface Approach to Viewing and Teaching Aqueous Equilibrium Chemistry. 2.
https://scholarworks.umt.edu/topos/2
Comments
This document is the Accepted Manuscript version of a Published Work that appeared in final form in the Journal of Chemical Education, copyright © American Chemical Society and the Division of Chemical Education, Inc., after peer review and technical editing by the publisher. Access the final edited and published work.